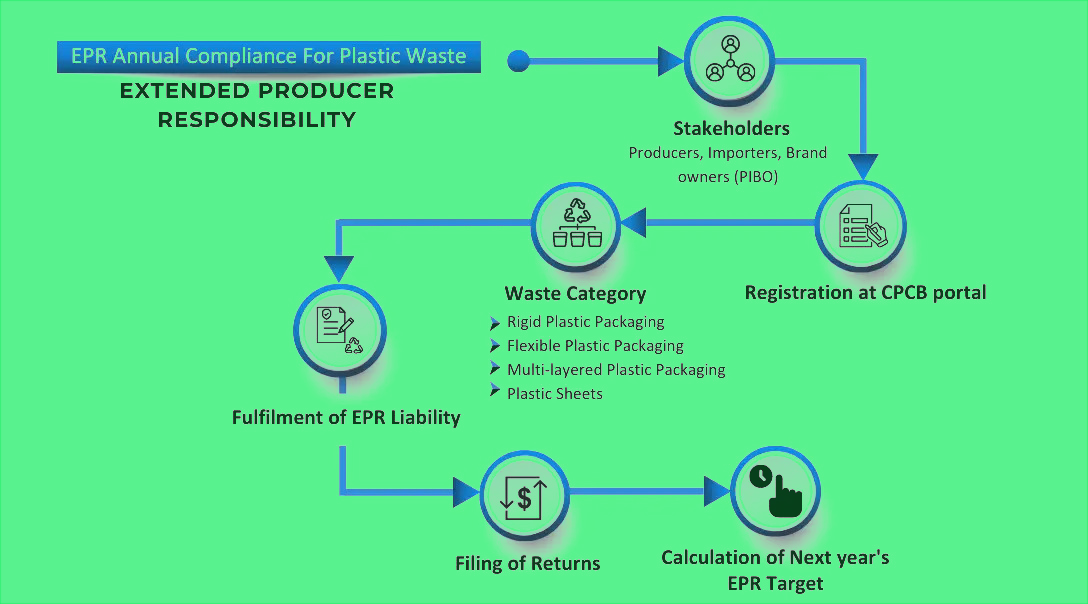
The growing concern over plastic pollution has led to the establishment of stringent regulations under the Plastic Waste Management (PWM) Rules, 2016, in India. These rules mandate Producers, Importers, and Brand Owners (PIBOs) to register with the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) or respective State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) and adhere to the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) framework. This blog delves into the significance of compliance, the impact of non-compliance, and available data from government reports.
Compliance Numbers and Impact
As of April 5, 2022, the CPCB reported that 36,230 PIBOs and 2,351 Plastic Waste Processors (PWPs) had registered through the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Portal. Despite the growing number of compliant entities, there remains a considerable gap, with many still unregistered.
Impact of Non-Compliance
- Legal Consequences:
- Non-compliance can lead to substantial penalties and legal actions under the Environmental Protection Act, 1986.
- Businesses operating without EPR registration may incur an Environmental Compensation (EC) of ₹5,000 per ton for the first violation, ₹10,000 per ton for the second, and ₹20,000 per ton for the third.
- Environmental Impact:
- India generates approximately 3.5 million tons of plastic waste annually, with only 60% being recycled. The rest ends up in landfills, water bodies, or is incinerated, causing severe environmental damage.
- Non-compliance exacerbates plastic pollution, leading to soil and water contamination, harm to marine and wildlife, and increased greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reputational Damage:
- Non-compliant companies risk damaging their brand image and losing consumer trust. According to a 2021 survey, 88% of consumers prefer brands that take environmental sustainability seriously.
- With rising awareness, investors are also leaning towards companies with strong environmental governance.
- Economic Impact:
- The improper management of plastic waste results in an estimated economic loss of $13 billion annually due to its impact on marine ecosystems.
- Non-compliance can lead to higher waste management costs and missed business opportunities, as environmentally conscious partnerships become more prevalent.
Government Reports and Guidelines
The CPCB’s Annual Report 2020-21 on Implementation of Plastic Waste Management Rules provides comprehensive data on plastic waste generation and the status of PWM implementation across India. It highlights the compliance status of various PIBOs and the progress made in different states and union territories.
Additionally, the CPCB has issued specific guidelines for assessing environmental compensation for violations of the PWM Rules. The document titled “Guidelines for Assessment of Environment Compensation to be levied for Violation of Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016” outlines the fines and legal actions applicable to violators, ensuring accountability and enforcement.
Additional Facts and Figures
- India’s per capita plastic consumption is around 11 kg per year, significantly lower than the global average of 28 kg, but rising rapidly.
- Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Gujarat are among the top states generating plastic waste, contributing to nearly 40% of the total plastic waste in India.
- The CPCB’s efforts have led to the closure of over 200 non-compliant units and the issuance of notices to several others.
- Plastic waste import: India imported approximately 12,000 tons of plastic waste in 2020, adding to the domestic burden.
- Global context: Worldwide, 300 million tons of plastic waste are generated annually, with only 9% recycled, underscoring the global challenge.
Conclusion
Adhering to the Plastic Waste Management Rules is crucial for businesses in India. It not only helps mitigate environmental impact but also ensures legal compliance and fosters a sustainable future. The growing number of registered PIBOs and PWPs is a positive sign, but continued efforts are essential to achieve comprehensive compliance and effective plastic waste management. For more detailed information, refer to the CPCB’s annual reports and guidelines available on their official website.
References
- CPCB Annual Report 2020-21 on Implementation of Plastic Waste Management Rules: Link
- Guidelines for Assessment of Environment Compensation to be levied for Violation of Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016: Link
- CPCB EPR Portal Registration Data: Link
- Consumer Survey on Environmental Sustainability, 2021: [Source]
- Economic Impact of Plastic Pollution: [Source]